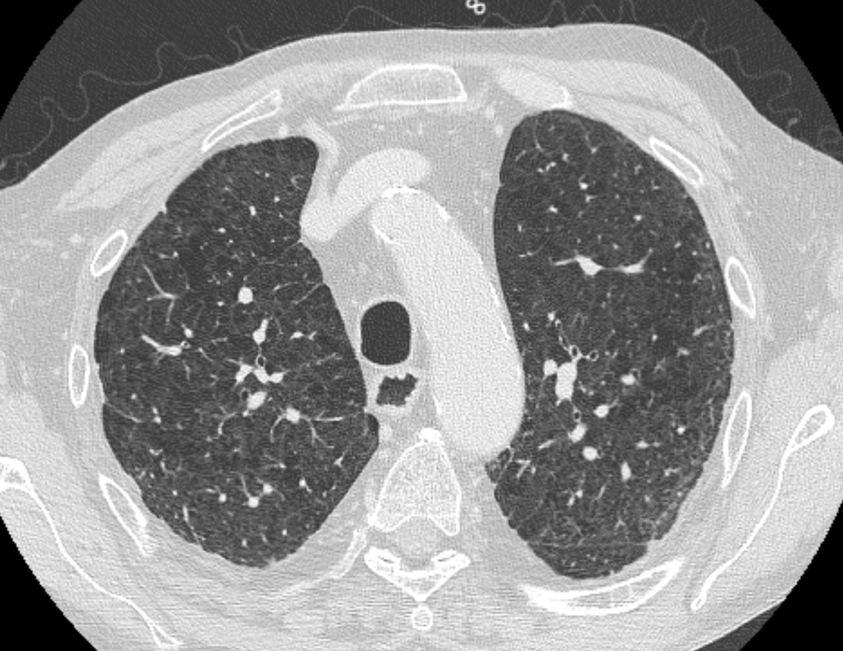
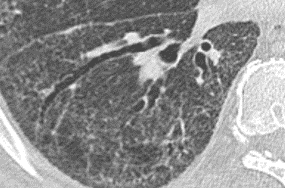
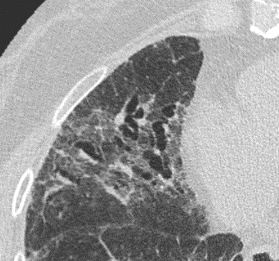
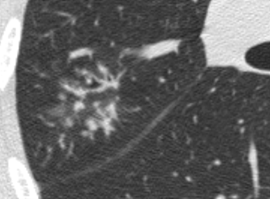
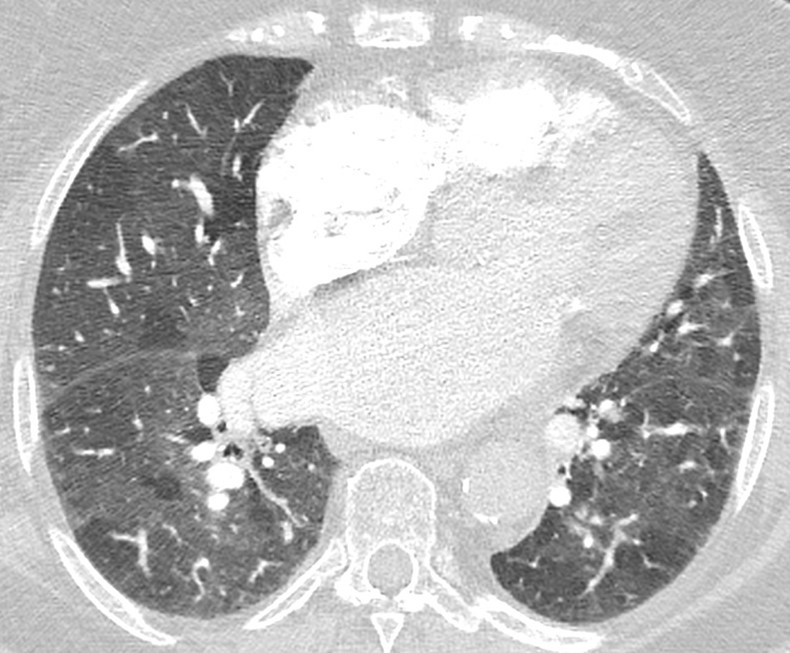
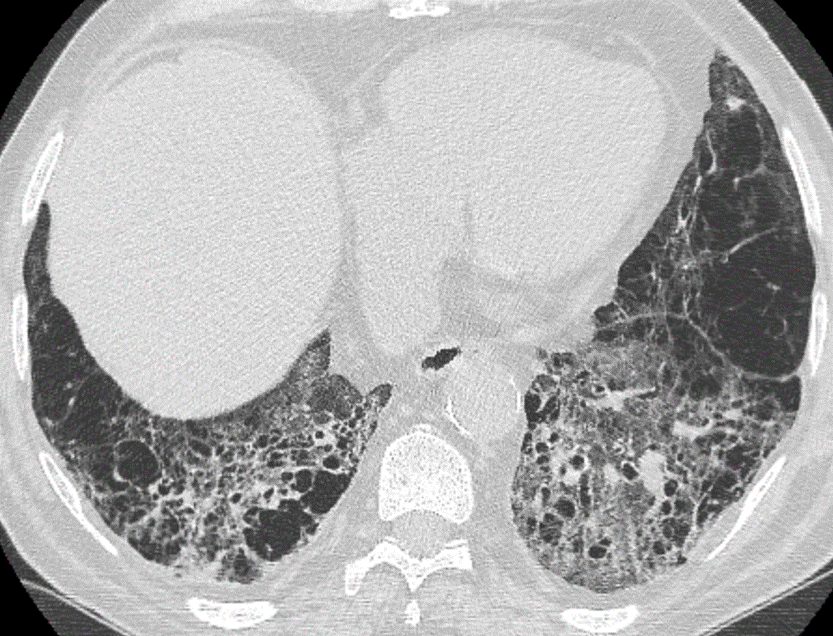
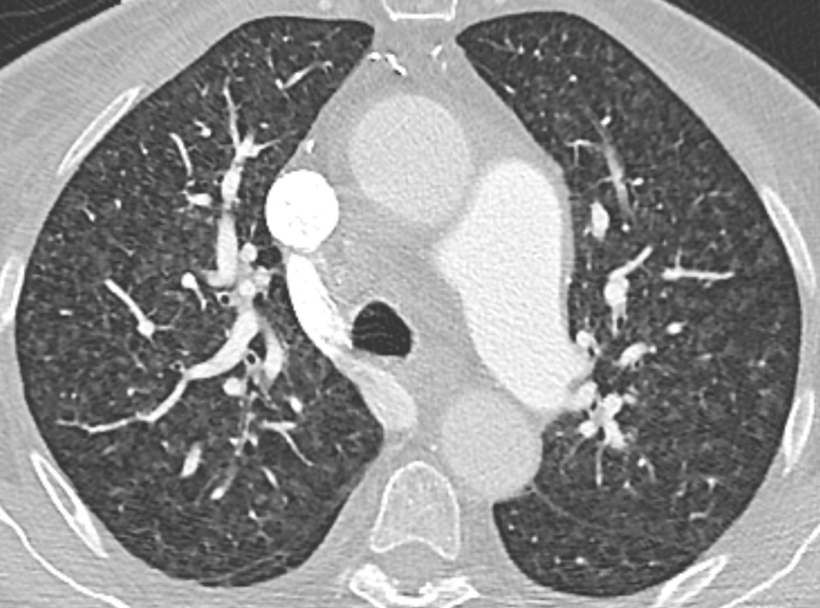
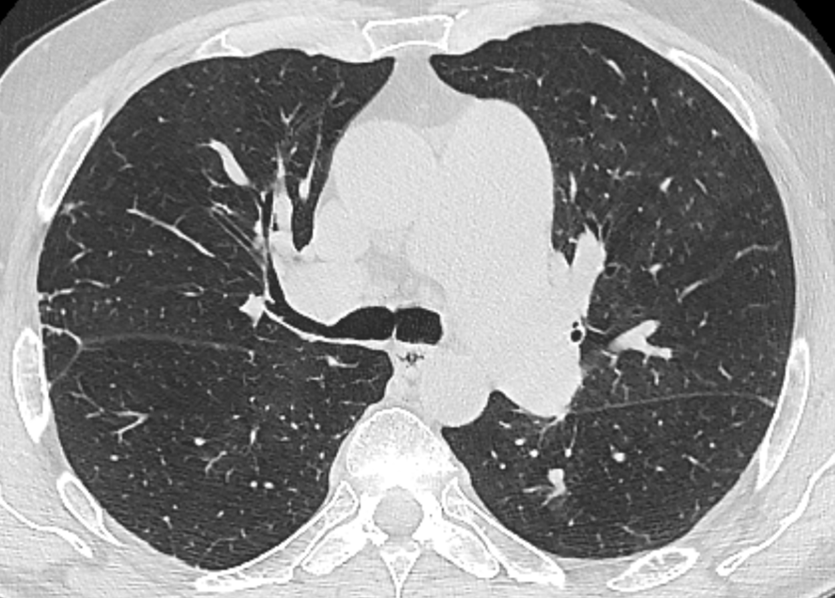
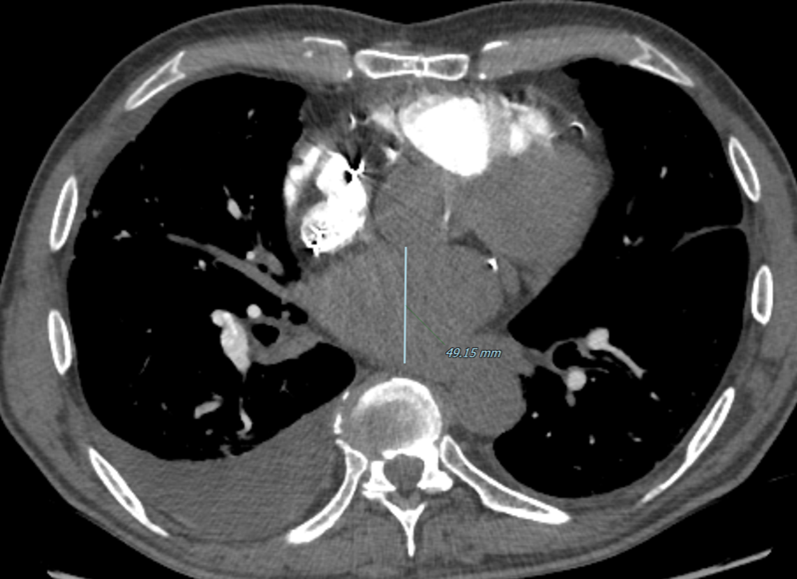
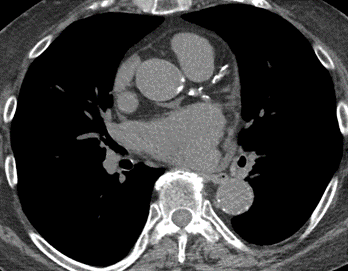
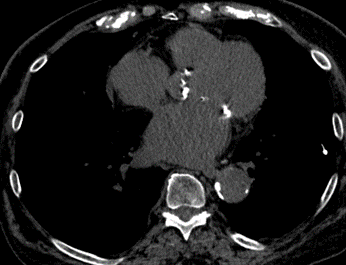
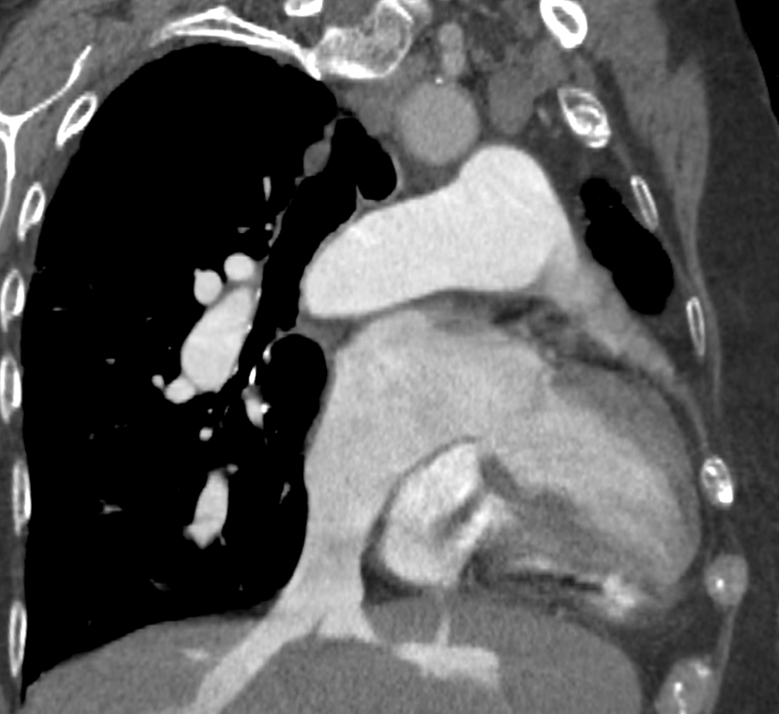
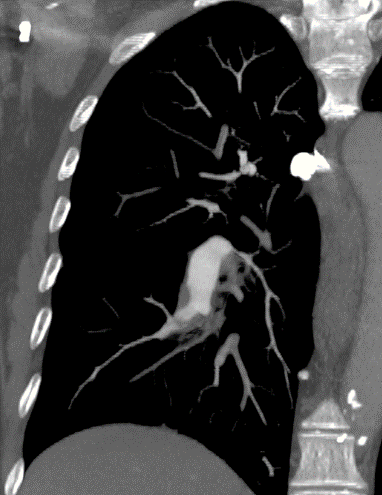
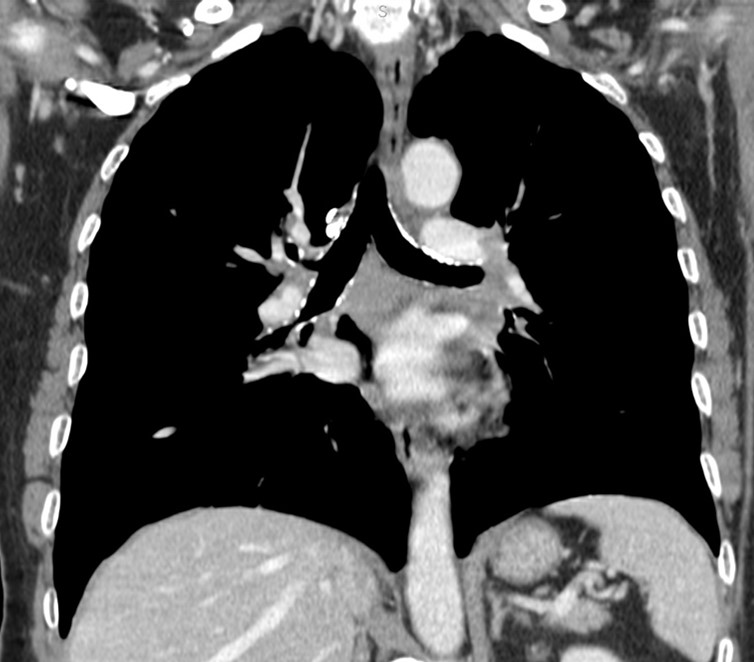
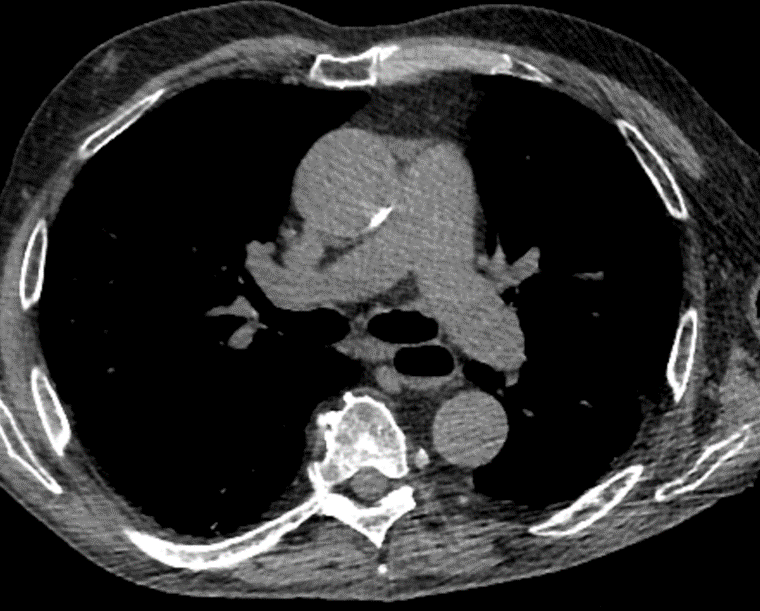
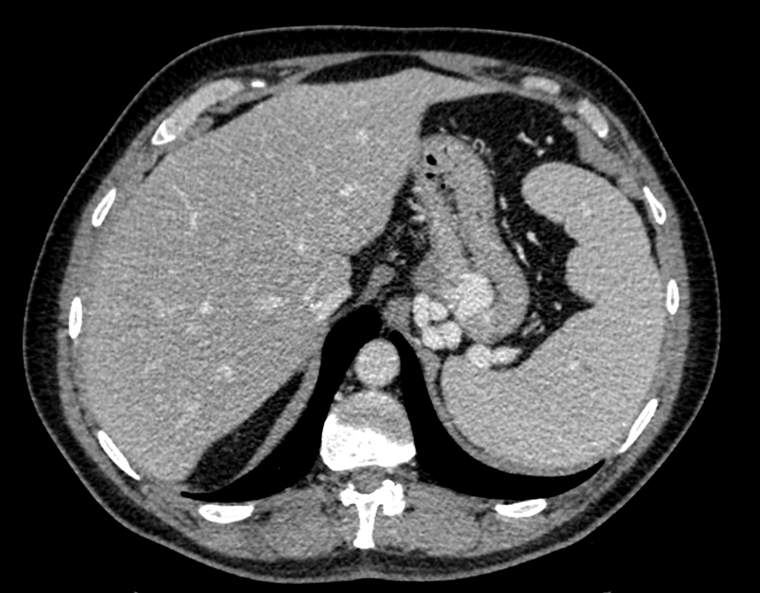
Nodules with centrilobular distribution locate a few millimeters away from the pleural surface and fissures, without direct contact with them. Diffusely distributed, poorly defined centrilobular ground-glass nodules are commonly observed in patients with idiopathic PAH. These nodules correspond to cholesterol granulomas resulting from the ingestion of red blood cells by pulmonary macrophages. The differential diagnosis includes hypersensitivity pneumonitis, respiratory bronchiolitis, follicular bronchiolitis, and long-standing left-to-right shunt. It is worth noting that centrilobular ground-glass nodules, along with tortuous corkscrew vessels, can also be observed in pulmonary capillary hemangiomatosis (PCH) and pulmonary veno-occlusive disease (PVOD).